Qtech Control
International Inspection Engineers, Cargo Surveyors and Technical Resources

Pump Inspection UK

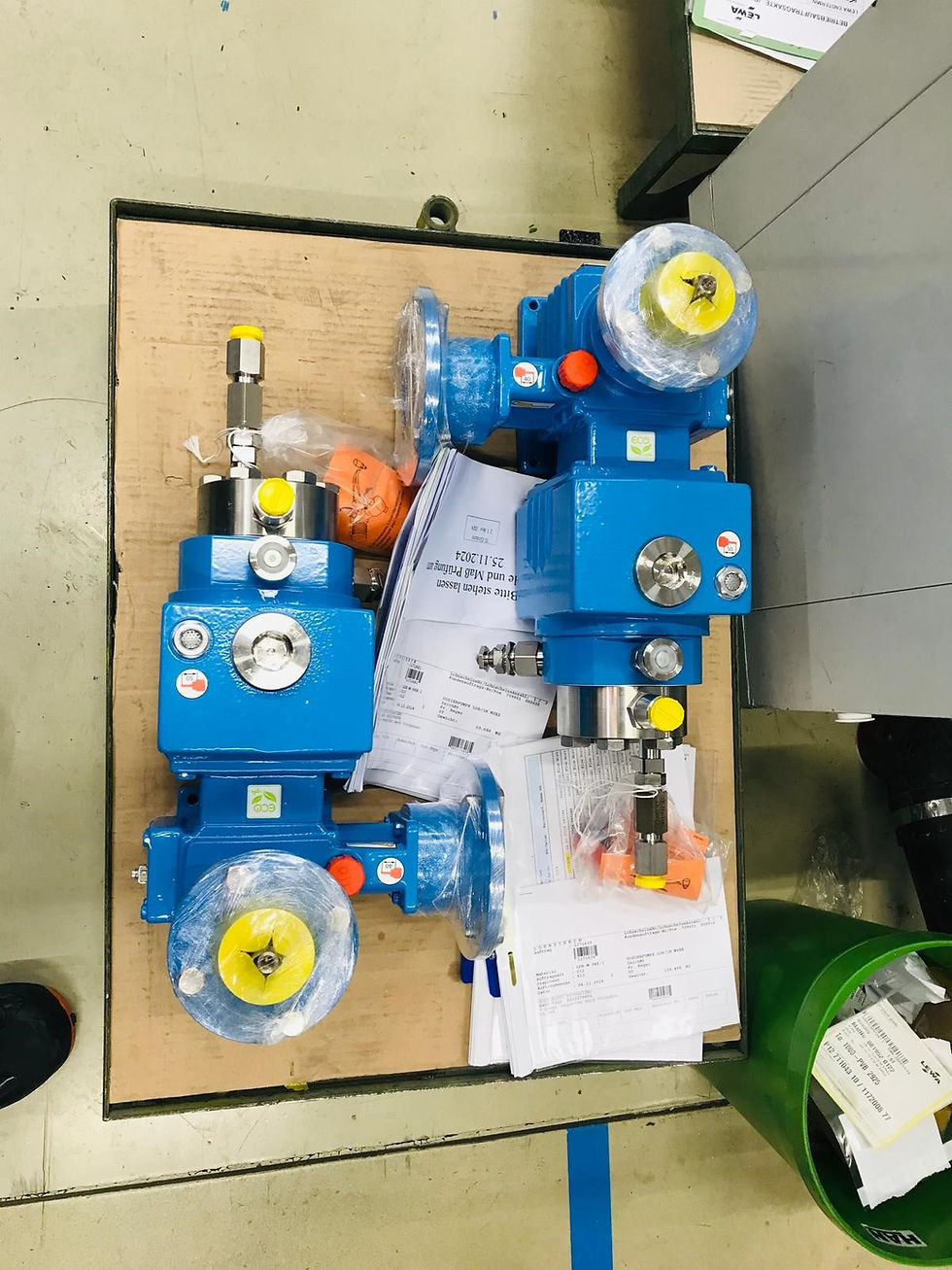
Pump Inspection Germany

Pump Inspection Italy

Pump Inspection Spain
Third Party Inspection And Witness Testing Of Pumps Worldwide
When carrying out a Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) for industrial pumps, the goal is to ensure that the equipment meets the design, performance, safety, and operational specifications agreed upon by both trading parties before the pump is shipped and installed.
Qtech Control provide highly experienced mechanical inspectors for witness testing and quality control of pumps at many of the world’s most prominent pump manufacturing sites.
We offer a comprehensive range of inspection services which we can tailor to meet the requirements of individual clients, however we generally attend vendor sites to witness pump Factory Acceptance Test following agreed test procedures and inspection test plans.
Overview of services provided at pump manufacturing sites:
-
Client Representation at Pre Inspection Meetings.
-
Material Testing, Traceability, Document Review.
-
Visual Inspection / Pump Identification.
-
Dimensional Control.
-
Witness Testing including: Performance Test, Sound Emission (Noise) Test, Vibration Test, Temperature Rise Test, Hydrostatic Pressure Test, Net Positive Suction Head Test (NPSH).
-
Coating Inspection, Tagging Inspection, MRB Review, Final Inspection.
-
Packing / Protection / Preservation and Marking Inspection.
Qtech Control is an ISO 17020 registered type A inspection body. Included in our accreditation is the inspection, testing and certification of pumps.

Pump Witness Testing Japan

Pump Inspection Japan
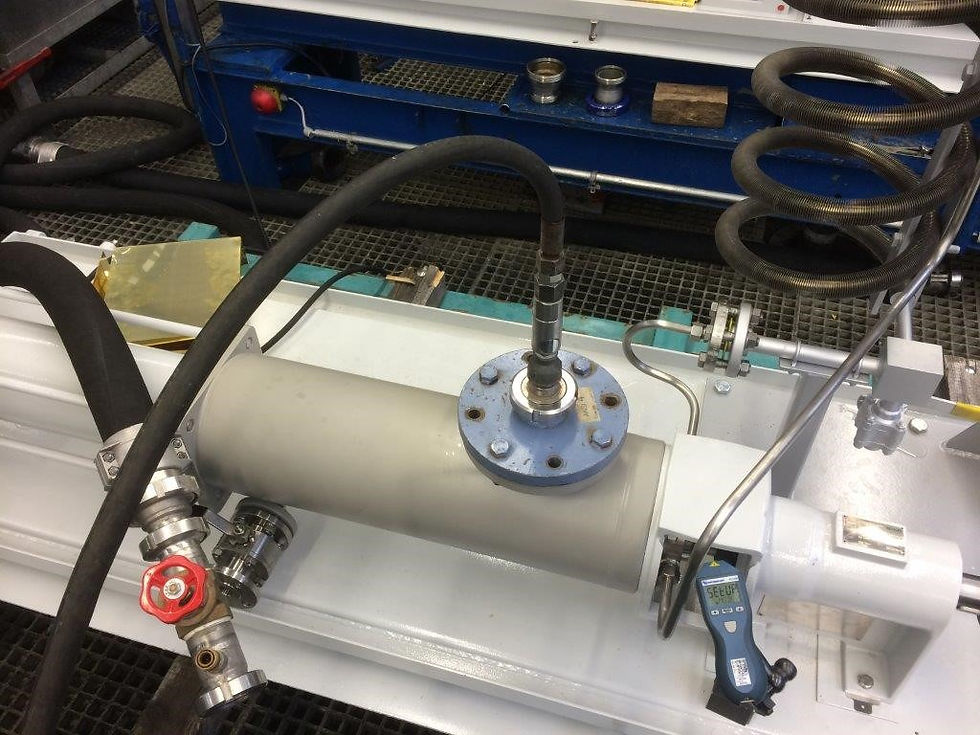
Pump Inspection UK
Example Pump Inspection Services


Pump Head


Vendor Sites Attended include:
-
Lewa Pumps, Leonberg, Germany
-
Flowserve, Newark, UK
-
Torishima Pump, Leamington Spa, UK
-
Torishima Pump, Osaka, Japan
-
Allweiler Pump, Radolfzell, Germany
-
Sulzer Pumps, Leeds, UK
-
Pumping And Technical Services, Macclesfield, UK
-
Ruthmann Pumpen, Baesweiler, Germany
-
Kloska Pump, Rostock, Germany
-
Bedford Pumps, Bedford, UK
-
SPP Pumps, Gloucester, UK
-
ITT Gould Pumps, Axminster, UK
-
Zhejiang Keer Pump Stock Co, Zhejiang, China
-
Holland Legacy Pump, Utrecht, Netherlands
-
Leistritz Pumps, Freiberg, Germany
-
Naffco, Jaslo, Poland
-
Pumpsets Ltd, Andover, UK
-
Veolia Wittell Pump, Stoke-on-Trent, UK
-
Pump Supply, Manchester, UK
-
Grundfos Manufacturing, Sunderland, UK
-
Sulzer Pumpen, Bruchsal, Germany
-
KSB Pumpen, Cardolzburg, Germany
-
Netzsch Pumpen, Waldkraiburg, Germany
Typical witness points for pump Factory Acceptance Test include:
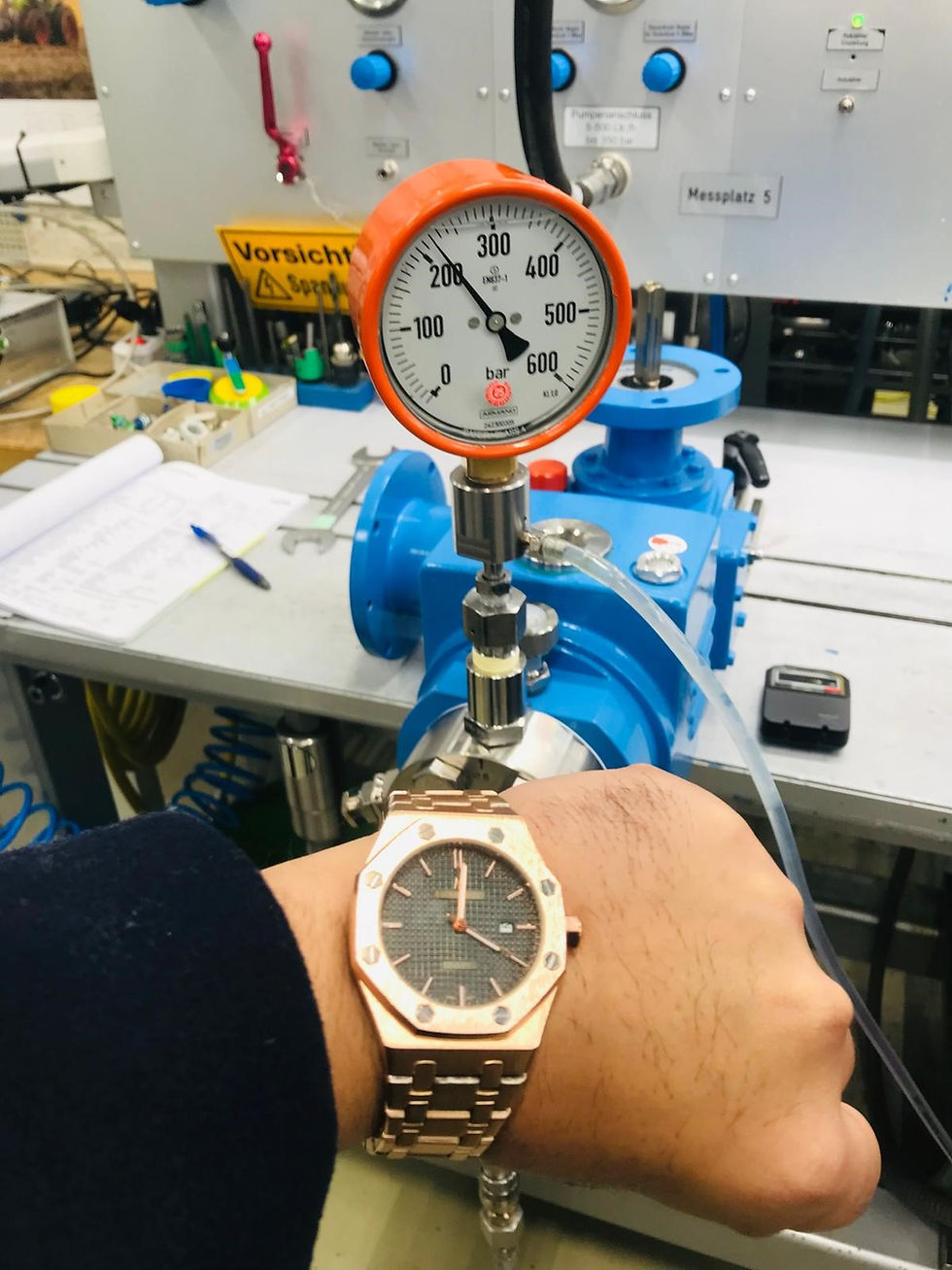
Hydrostatic (Leak) Test
To prevent downtime and environmental issues, it’s critical to simulate operating conditions that could challenge seal integrity. These tests confirm that the seals, gaskets, and other leak-prevention components are installed correctly and operate as expected without allowing fluid leakage.
The hydrostatic test procedure ensures that the pump heads are subjected to the required test pressure to confirm the integrity of the pump assembly. Preparations involve carefully sealing all openings with calibrated blind flanges, gaskets, and screws designed to withstand the specified test pressures. Pressure gauges, a control gauge, and a shut-off valve are installed to monitor the process. Proper venting of the pump heads is conducted to avoid pressure drops due to trapped air. The test fluid used is checked against the procedure.
The pump is hydrostatic pressure tested for the stipulated time period, during which the pressure is checked to ensure it is maintained at the specified level. The is monitored and checked for leakage during the hydrostatic test.
Mechanical Run Test
The pump is run at various speeds and loads to record its performance curve. These values are compared with the design specifications and contractual guarantees to ensure that the pump achieves the correct fluid flow and pressure (head) across its operating range.
During the mechanical run test the pump is usually monitored for unusual abnormalities such as noises, vibrations, or mechanical damage. The temperatures of the drive units are also checked to ensure they remain within acceptable limits.
Temperature Rise Test
The temperature at the bearing housing is measured until they reach almost constant value at speed and capacity specified in the agreed test procedure. The procedure states the temperature at which it shall not increase more than above ambient temperature.
Sound Emission (Noise) Test (Airbourne Sound)
The noise test measures sound levels generated during pump operation to ensure compliance with approved data sheets. The pump is set up on a test bench, and sound pressure levels are measured from both the front and back of the pump at a distance specified in the test procedure (usually 1 meter), aligned with the plunger axis. The sound levels are recorded in dB, and checked to ensure that they are within the permissible limit as specified in the test procedure and acceptance criteria.
Vibration Test
The vibration test determines mechanical vibrations exerted by the pump, and provides information about the running quality and vibration stress levels of connected parts such as pipes, base plates and foundations. The test is usually conducted for three kinds of direction (horizontal, vertical, axial) on both the pump and the motor.
High Discharge Pressure Test
This test ensures that the pump can operate safely and efficiently at high-pressure conditions without failure. The pump were is usually tested at 1.1 times their maximum operating pressure for a minimum period as specified in the agree test procedure. The test pressure is usually achieved using water with a chloride content below 30 ppm, and the pump is usually operated at maximum rated speed. The pump is monitored for possible leaks or operational issues under the high-pressure conditions.
Net Positive Inlet Pressure (NPIP) Test - Net Positive Suction Head Test (NPSH) Test
These tests verify the pumps capability to operate without cavitation under varying inlet pressures. Temporary piping is utilized to replicate field conditions, and the pump vapor pressure (Pvp) is determined. The results are checked to confirm that they are within acceptable limits, confirming their ability to maintain optimal performance under these conditions if so.
Visual and Dimensional Inspection
After completing the performance and functional tests, a thorough visual and dimensional inspection is usually conducted. The pump is examined for structural integrity, and the dimensional data is cross-verified with the technical specifications. Additionally, markings and nameplates are checked for accuracy and compliance with client requirements.
Final Inspection
During a final inspection the following items are typically checked:
-
Correct assembly.
-
Tag plate / labelling.
-
Completeness check of tests and delivered parts
-
Painting (Dry Film Thickness), Painting Color against RAL sample or chart
-
Rust Prevention Application.
Documentation Review
Document Review for pumps would typically consists of reviewing:
-
PMI (Positive Material Identification) reports.
-
Dye Penetration Test (DPT) reports.
-
Calibration Certificates for test instruments.
-
Water Analysis Certificate confirming chloride content as specified in the test procedure.
-
Test Reports as detailed above.

Pump Witness Testing Germany
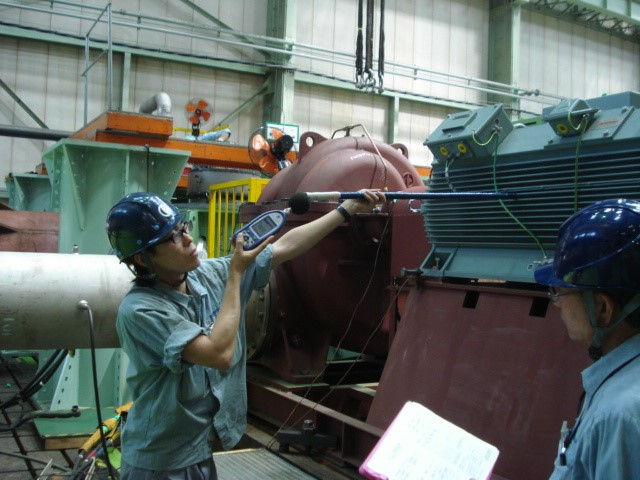

Pump Witness Testing Japan

Pump Witness Testing UK

Pump Witness Testing Germany

Pump Inspection UK
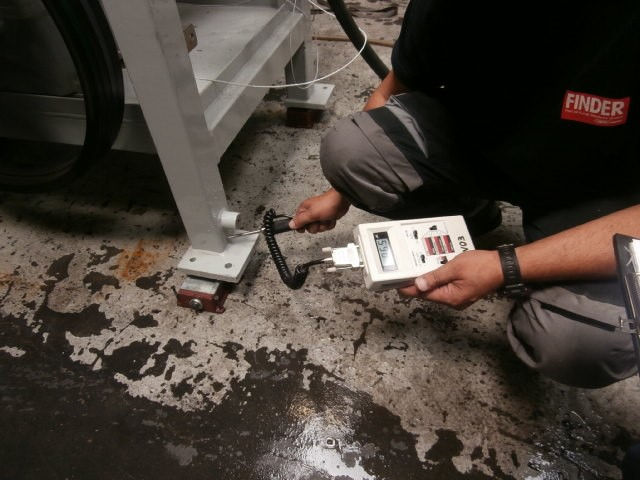

Pump Inspection Finland

Pump Inspection UK
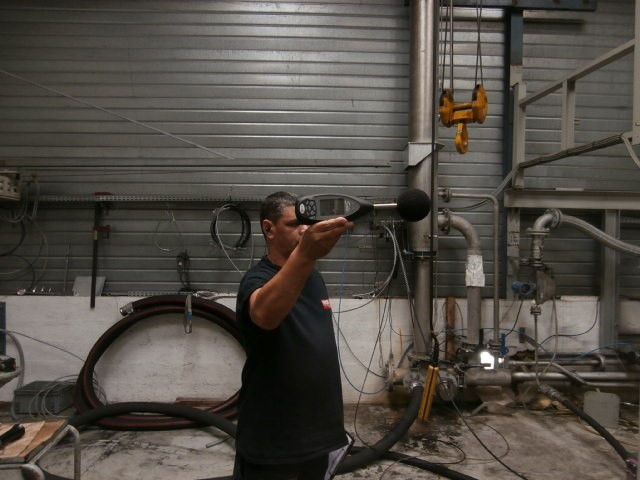

Pump Inspection France
